Malware and Phishing Domain Trends in 2024
Oct 17, 2024
Summary
In 2024, the landscape of phishing and spam-associated domains has seen significant changes, primarily influenced by global political and economic events. With the ongoing Russia-Ukraine conflict, there has been a surge in cybercrime activities, including the registration of phishing domains targeting various geopolitical entities. As these domains proliferate, threat actors exploit them for malicious campaigns, including phishing, fraud, and malware distribution. This article explores the trends in the registration of phishing and spam domains, the impact of the Russia-Ukraine war on these activities, and methods for identifying these domains.
Impact of the Russia-Ukraine Conflict on Phishing and Spam Domains
The Russia-Ukraine conflict has had a notable impact on cyber activities globally. The invasion has catalyzed the rise of phishing domains targeting Ukraine and its allies, often used for espionage and misinformation. Threat actors, such as the MOONSCAPE group, are linked to phishing campaigns directed at military and government personnel in Eastern Europe, particularly Ukraine and Poland. These domains are typically designed to impersonate legitimate entities, leveraging social engineering tactics to steal sensitive information or distribute malware
Reports from cybersecurity firms have shown that since the onset of the invasion, thousands of new domains have been registered, many of them containing terms related to Ukraine or its geopolitical context. For example, in the first quarter of 2024, the number of domains related to Ukraine surged by 210% compared to the previous year, with an average of 315 new Ukraine-themed domains registered per day. A significant portion of these were used for malicious purposes, including phishing and spam campaigns
Identification of Phishing and Spam Domains
Phishing domains are typically registered to resemble legitimate websites closely, often using slight variations in spelling or domain extensions to deceive users. Some common indicators that can help identify phishing domains include:
Domain Age: Newly registered domains are often associated with phishing or malicious activities. Tools like WHOIS can be used to check domain registration dates.
Suspicious TLDs: Certain top-level domains (TLDs) are frequently associated with malicious activities. For instance, TLDs like .top, .work, and .xyz are often linked to phishing domains.
SSL Certificates: While many legitimate websites use SSL certificates (HTTPS), the presence of SSL alone does not confirm the site's authenticity. Threat actors frequently obtain basic SSL certificates to give their phishing sites an air of legitimacy.
Content and Branding: Look for inconsistencies in logos, spelling, and grammar on the website. Phishing domains often copy legitimate websites but contain small errors that can reveal their true nature.
TLDs and Domain Categories in 2024
According to the DomainTools 2024 report, the types of TLDs most frequently associated with phishing and spam campaigns have shown significant shifts. Emerging regions such as Belize and Brazil have become hotbeds for phishing domains, while legacy TLDs like .com and .net continue to feature prominently in global phishing campaigns. A breakdown of the types of domains registered for phishing, spam, and malware activities in 2024 is provided in the table below:
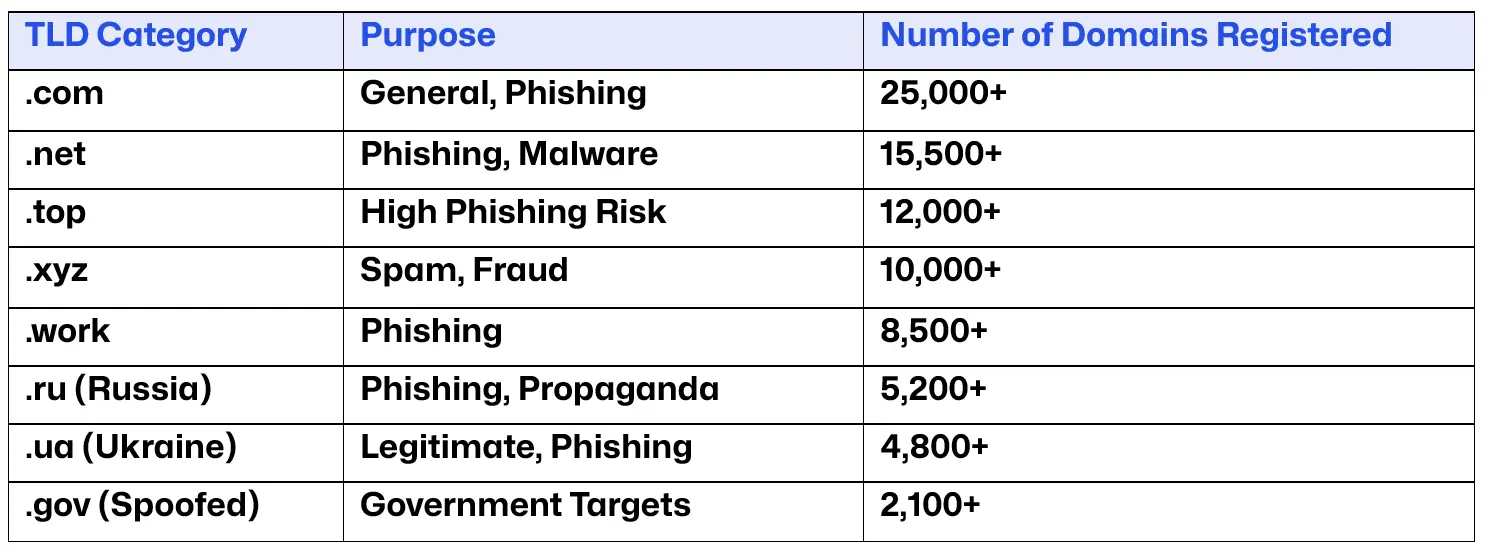
The report also highlights that the majority of phishing and spam domains are concentrated in specific TLDs known for being low-cost and less regulated. TLDs like .top, .xyz, and .work are particularly susceptible to abuse by cybercriminals
Phishing and Malware Trends
The DomainTools 2024 report also categorizes the rise in malware-associated domains. Brazil has experienced a notable increase, with over 17,000 malware-related domains registered, marking a significant jump from previous years. The table below illustrates the signal strength and categories of various TLDs in relation to malware.
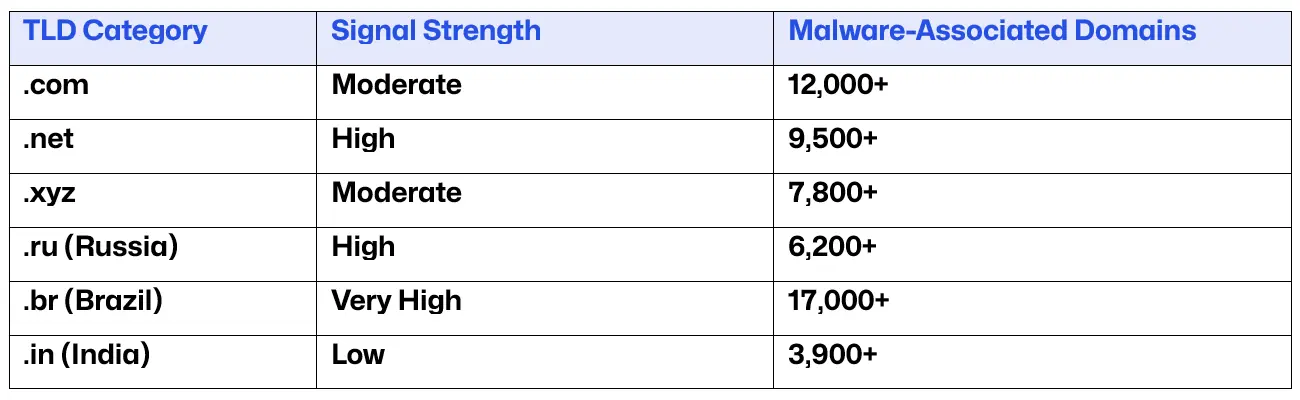
Conclusion
The registration of phishing and spam domains has seen a substantial increase in 2024, influenced largely by geopolitical factors such as the Russia-Ukraine conflict. Cybercriminals continue to exploit global crises to target vulnerable populations, with phishing domains often being used for espionage, fraud, and malware distribution. As phishing tactics evolve, it remains crucial for individuals and organizations to be vigilant in identifying malicious domains and implementing comprehensive security measures.
The global cybersecurity community must remain proactive in monitoring and reporting new domain registrations, particularly those associated with TLDs known for high malicious activity, to mitigate the risks posed by these campaigns